Products
Locking plate
WASTON
30723
3/5/7/9/11/13
105/145/185/225/265/305
Ti
30723
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |








| Code | Holes | Length | ||
| 30723-003 | L | 3 | 105 | |
| 30723-103 | R | |||
| 30723-005 | L | 5 | 145 | |
| 30723-105 | R | |||
| 30723-007 | L | 7 | 185 | |
| 30723-107 | R | |||
| 30723-009 | L | 9 | 225 | |
| 30723-109 | R | |||
| 30723-011 | L | 11 | 265 | |
| 30723-111 | R | |||
| 30723-013 | L | 13 | 305 | |
| 30723-113 | R | |||
Anatomical Contouring: The plate is precontoured to match the lateral aspect of the proximal tibia, reducing the need for intraoperative bending and ensuring an optimal fit.
Locking Mechanism: Equipped with threaded holes for locking screws, providing angular stability and minimizing the risk of screw loosening.
Low-Profile Design: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Combination Holes: Supports both locking and non-locking (cortical) screws, offering versatile fixation options.
Polyaxial Locking: Allows for variable angle screw placement, enhancing flexibility during surgery.
Biocompatible Materials: Typically made from titanium alloy or stainless steel, ensuring durability, strength, and compatibility with the human body.
Locking Screws: Designed to work with 5.0 mm locking screws.
Non-Locking Screws: Can also accommodate non-locking (cortical) screws for additional fixation options.
Thickness: Approximately 3.5 mm to 4.0 mm, providing a balance between strength and flexibility.
Width and Length: Varies depending on the plate size to fit different patient anatomies and fracture patterns.
Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) Capability: Designed to be used with minimally invasive surgical techniques, reducing soft tissue disruption and promoting quicker recovery.
Radiolucent Markers: Some versions include radiolucent markers to aid in precise screw placement under imaging guidance.
Multiple Screw Holes: The plate includes multiple screw holes to provide adequate fixation points for complex fracture patterns.
Enhanced Fit: The anatomical contouring provides a closer fit to the bone, reducing the need for intraoperative adjustments and improving surgical outcomes.
Enhanced Fixation Stability: Locking screws provide rigid fixation, which is particularly beneficial in osteoporotic bone.
Improved Anatomical Fit: Precontoured design improves the fit and alignment, saving surgical time and improving outcomes.
Versatility in Fixation: Combination holes and polyaxial screw placement offer flexibility in surgical techniques and fixation methods.
Reduced Soft Tissue Irritation: Low-profile design minimizes soft tissue irritation and postoperative complications.
Promotes Faster Recovery: MIS capability reduces soft tissue disruption, leading to faster recovery times.
The 5.0mm Proximal Lateral Tibial Golf Locking Compression Plate is designed for the fixation of fractures and other conditions affecting the proximal lateral tibia. Here are the primary indications for its use:
Intra-articular Fractures: Fractures that involve the tibial plateau and extend into the joint, requiring precise anatomical reduction and stable fixation.
Extra-articular Fractures: Fractures that do not extend into the joint but still require stable fixation for proper healing.
Comminuted Fractures: Fractures where the bone is broken into multiple pieces, necessitating a stable and secure fixation method.
Displaced Fractures: Fractures where the bone fragments are misaligned and need to be repositioned and stabilized.
Elderly Patients: In patients with poor bone quality due to osteoporosis, the locking mechanism provides enhanced stability and reduces the risk of screw loosening.
Pathologic Fractures: Fractures occurring in bones weakened by disease, such as cancer or infection, where secure fixation is crucial.
Corrective Osteotomies: Surgical procedures to correct malunions (healed fractures in improper alignment) or nonunions (fractures that fail to heal) of the proximal tibia.
Multifragmentary Fractures: Fractures with multiple fragments where stable fixation and precise alignment are necessary to restore function.
Corrective Surgery for Deformities: Procedures to correct deformities of the proximal tibia, which may be congenital or acquired.
Fractures with Soft Tissue Injury: Open fractures where the bone is exposed through a wound, requiring rigid fixation and minimal soft tissue disruption to promote healing.
Fractures Near Joints: Fractures near the knee joint that need stable fixation to ensure proper healing and restore joint function.
Complex High-Energy Fractures: Fractures resulting from high-energy trauma, such as motor vehicle accidents, where stable and secure fixation is crucial for proper healing.
Enhanced Fixation Stability: The locking screws provide rigid fixation, which is particularly beneficial in osteoporotic or poor-quality bone.
Improved Anatomical Fit: The precontoured design improves the fit and alignment, saving surgical time and improving outcomes.
Versatility in Fixation: Combination holes and polyaxial screw placement offer flexibility in surgical techniques and fixation methods.
Reduced Soft Tissue Irritation: The low-profile design minimizes soft tissue irritation and postoperative complications.
Promotes Faster Recovery: The ability to use minimally invasive surgical (MIS) techniques reduces soft tissue disruption, leading to faster recovery times
Multiple Screw Angles: Allows for multi-directional screw placement to accommodate different fracture patterns and ensure secure fixation.
Polyaxial Locking: Facilitates variable angle screw placement, enhancing flexibility during surgery.
These indications ensure that the 5.0mm Proximal Lateral Tibial Golf Locking Compression Plate provides effective and reliable fixation for a variety of fractures and deformities, catering to a wide range of clinical scenarios and patient anatomies.
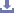
The plate is used for the fixation of fractures in the proximal lateral tibia, including periarticular fractures, osteoporotic bone fractures, and fractures involving the metaphyseal region.
The plate is typically made from biocompatible materials such as titanium alloy or stainless steel, ensuring strength, durability, and compatibility with the human body.
The plate thickness is approximately 3.5 mm to 4.0 mm, providing a balance between strength and flexibility.
The plate is designed to work with 5.0 mm locking screws and can also accommodate non-locking (cortical) screws for additional fixation options.
The locking mechanism includes threaded holes for locking screws, ensuring angular stability, reducing the risk of screw loosening, and providing more stable fixation compared to conventional plates.
The anatomical contouring matches the lateral aspect of the proximal tibia, reducing the need for intraoperative bending, improving fit and alignment, and saving surgical time.
The low-profile design minimizes soft tissue irritation and reduces the risk of postoperative complications, promoting faster and more comfortable recovery for the patient.
Yes, the plate is designed to be used with minimally invasive surgical techniques, reducing soft tissue disruption and promoting quicker recovery.
Polyaxial locking allows screws to be placed at various angles, providing flexibility in screw placement, accommodating different fracture patterns, and enhancing fixation stability.
Some versions of the plate include radiolucent markers to aid in precise screw placement under imaging guidance.
Enhanced Fixation Stability: Locking screws provide rigid fixation, particularly useful in osteoporotic bone.
Improved Anatomical Fit: Precontoured design improves the fit and reduces the need for intraoperative adjustments.
Versatility: Combination holes and polyaxial screw placement offer flexibility in surgical techniques and fixation methods.
Minimized Soft Tissue Irritation: Low-profile design minimizes irritation and postoperative complications.
Promotes Faster Recovery: MIS capability reduces soft tissue disruption, leading to faster recovery times.
The plate typically has multiple screw holes in the proximal segment for secure fixation of the metaphyseal region and a series of holes along the shaft for diaphyseal fixation. The exact number varies depending on the plate length.
Yes, the locking mechanism provides enhanced stability and is particularly beneficial in osteoporotic bone, where conventional screws may not hold as effectively.
| Code | Holes | Length | ||
| 30723-003 | L | 3 | 105 | |
| 30723-103 | R | |||
| 30723-005 | L | 5 | 145 | |
| 30723-105 | R | |||
| 30723-007 | L | 7 | 185 | |
| 30723-107 | R | |||
| 30723-009 | L | 9 | 225 | |
| 30723-109 | R | |||
| 30723-011 | L | 11 | 265 | |
| 30723-111 | R | |||
| 30723-013 | L | 13 | 305 | |
| 30723-113 | R | |||
Anatomical Contouring: The plate is precontoured to match the lateral aspect of the proximal tibia, reducing the need for intraoperative bending and ensuring an optimal fit.
Locking Mechanism: Equipped with threaded holes for locking screws, providing angular stability and minimizing the risk of screw loosening.
Low-Profile Design: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Combination Holes: Supports both locking and non-locking (cortical) screws, offering versatile fixation options.
Polyaxial Locking: Allows for variable angle screw placement, enhancing flexibility during surgery.
Biocompatible Materials: Typically made from titanium alloy or stainless steel, ensuring durability, strength, and compatibility with the human body.
Locking Screws: Designed to work with 5.0 mm locking screws.
Non-Locking Screws: Can also accommodate non-locking (cortical) screws for additional fixation options.
Thickness: Approximately 3.5 mm to 4.0 mm, providing a balance between strength and flexibility.
Width and Length: Varies depending on the plate size to fit different patient anatomies and fracture patterns.
Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) Capability: Designed to be used with minimally invasive surgical techniques, reducing soft tissue disruption and promoting quicker recovery.
Radiolucent Markers: Some versions include radiolucent markers to aid in precise screw placement under imaging guidance.
Multiple Screw Holes: The plate includes multiple screw holes to provide adequate fixation points for complex fracture patterns.
Enhanced Fit: The anatomical contouring provides a closer fit to the bone, reducing the need for intraoperative adjustments and improving surgical outcomes.
Enhanced Fixation Stability: Locking screws provide rigid fixation, which is particularly beneficial in osteoporotic bone.
Improved Anatomical Fit: Precontoured design improves the fit and alignment, saving surgical time and improving outcomes.
Versatility in Fixation: Combination holes and polyaxial screw placement offer flexibility in surgical techniques and fixation methods.
Reduced Soft Tissue Irritation: Low-profile design minimizes soft tissue irritation and postoperative complications.
Promotes Faster Recovery: MIS capability reduces soft tissue disruption, leading to faster recovery times.
The 5.0mm Proximal Lateral Tibial Golf Locking Compression Plate is designed for the fixation of fractures and other conditions affecting the proximal lateral tibia. Here are the primary indications for its use:
Intra-articular Fractures: Fractures that involve the tibial plateau and extend into the joint, requiring precise anatomical reduction and stable fixation.
Extra-articular Fractures: Fractures that do not extend into the joint but still require stable fixation for proper healing.
Comminuted Fractures: Fractures where the bone is broken into multiple pieces, necessitating a stable and secure fixation method.
Displaced Fractures: Fractures where the bone fragments are misaligned and need to be repositioned and stabilized.
Elderly Patients: In patients with poor bone quality due to osteoporosis, the locking mechanism provides enhanced stability and reduces the risk of screw loosening.
Pathologic Fractures: Fractures occurring in bones weakened by disease, such as cancer or infection, where secure fixation is crucial.
Corrective Osteotomies: Surgical procedures to correct malunions (healed fractures in improper alignment) or nonunions (fractures that fail to heal) of the proximal tibia.
Multifragmentary Fractures: Fractures with multiple fragments where stable fixation and precise alignment are necessary to restore function.
Corrective Surgery for Deformities: Procedures to correct deformities of the proximal tibia, which may be congenital or acquired.
Fractures with Soft Tissue Injury: Open fractures where the bone is exposed through a wound, requiring rigid fixation and minimal soft tissue disruption to promote healing.
Fractures Near Joints: Fractures near the knee joint that need stable fixation to ensure proper healing and restore joint function.
Complex High-Energy Fractures: Fractures resulting from high-energy trauma, such as motor vehicle accidents, where stable and secure fixation is crucial for proper healing.
Enhanced Fixation Stability: The locking screws provide rigid fixation, which is particularly beneficial in osteoporotic or poor-quality bone.
Improved Anatomical Fit: The precontoured design improves the fit and alignment, saving surgical time and improving outcomes.
Versatility in Fixation: Combination holes and polyaxial screw placement offer flexibility in surgical techniques and fixation methods.
Reduced Soft Tissue Irritation: The low-profile design minimizes soft tissue irritation and postoperative complications.
Promotes Faster Recovery: The ability to use minimally invasive surgical (MIS) techniques reduces soft tissue disruption, leading to faster recovery times
Multiple Screw Angles: Allows for multi-directional screw placement to accommodate different fracture patterns and ensure secure fixation.
Polyaxial Locking: Facilitates variable angle screw placement, enhancing flexibility during surgery.
These indications ensure that the 5.0mm Proximal Lateral Tibial Golf Locking Compression Plate provides effective and reliable fixation for a variety of fractures and deformities, catering to a wide range of clinical scenarios and patient anatomies.
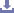
The plate is used for the fixation of fractures in the proximal lateral tibia, including periarticular fractures, osteoporotic bone fractures, and fractures involving the metaphyseal region.
The plate is typically made from biocompatible materials such as titanium alloy or stainless steel, ensuring strength, durability, and compatibility with the human body.
The plate thickness is approximately 3.5 mm to 4.0 mm, providing a balance between strength and flexibility.
The plate is designed to work with 5.0 mm locking screws and can also accommodate non-locking (cortical) screws for additional fixation options.
The locking mechanism includes threaded holes for locking screws, ensuring angular stability, reducing the risk of screw loosening, and providing more stable fixation compared to conventional plates.
The anatomical contouring matches the lateral aspect of the proximal tibia, reducing the need for intraoperative bending, improving fit and alignment, and saving surgical time.
The low-profile design minimizes soft tissue irritation and reduces the risk of postoperative complications, promoting faster and more comfortable recovery for the patient.
Yes, the plate is designed to be used with minimally invasive surgical techniques, reducing soft tissue disruption and promoting quicker recovery.
Polyaxial locking allows screws to be placed at various angles, providing flexibility in screw placement, accommodating different fracture patterns, and enhancing fixation stability.
Some versions of the plate include radiolucent markers to aid in precise screw placement under imaging guidance.
Enhanced Fixation Stability: Locking screws provide rigid fixation, particularly useful in osteoporotic bone.
Improved Anatomical Fit: Precontoured design improves the fit and reduces the need for intraoperative adjustments.
Versatility: Combination holes and polyaxial screw placement offer flexibility in surgical techniques and fixation methods.
Minimized Soft Tissue Irritation: Low-profile design minimizes irritation and postoperative complications.
Promotes Faster Recovery: MIS capability reduces soft tissue disruption, leading to faster recovery times.
The plate typically has multiple screw holes in the proximal segment for secure fixation of the metaphyseal region and a series of holes along the shaft for diaphyseal fixation. The exact number varies depending on the plate length.
Yes, the locking mechanism provides enhanced stability and is particularly beneficial in osteoporotic bone, where conventional screws may not hold as effectively.
