Products
Locking Comprssion plate
WASTON
70746
6
Ti
70746
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |








| Code | Holes | ||||
| 70746-006 | 6 | ||||
Anatomical Design:
Shape and Contour: Designed to fit the anatomy of the sacroiliac joint, ensuring proper alignment and stability.
Material:
Biocompatible: Typically made from materials like titanium alloy or stainless steel, ensuring compatibility with the human body.
Compression Mechanism:
Compression Slots/Holes: Includes slots or holes to allow for compression at the fracture site, aiding in bone healing and stability.
Locking Mechanism:
Locking Screws: Utilizes locking screws that engage with the plate, providing angular stability and reducing the risk of screw loosening.
Plate Thickness and Profile:
Low-profile Design: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Versatility:
Various Sizes: Available in different sizes to accommodate varying patient anatomies and fracture types.
Multiple Holes: Provides flexibility in screw placement to adapt to different fracture patterns and surgical techniques.
Surgical Technique:
Placement: Requires precise surgical placement to ensure proper alignment and effective compression of the joint.
Clinical Application:
Fracture Fixation: Used primarily for stabilizing fractures of the sacrum or ilium involving the sacroiliac joint.
Joint Fusion: Can also be used in procedures aimed at achieving fusion of the sacroiliac joint.
Postoperative Considerations:
Recovery: Patients may undergo physical therapy to regain strength and mobility after surgery.
Long-term Use: In some cases, the plate may remain in place permanently if it does not cause discomfort or complications.
Stability: Provides stable fixation, crucial for fractures or injuries affecting the sacroiliac joint.
Biomechanical Support: Restores biomechanical alignment of the joint, aiding in functional recovery.
Reduced Complications: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and promotes faster healing due to its low-profile design.
Customization: Offers options in size and configuration to meet individual patient needs and surgical requirements.
Always consult with a healthcare professional or orthopedic surgeon for specific medical advice and treatment options related to sacroiliac fractures or injuries.
Complex Fractures:
Comminuted Fractures: Fractures where the bone is broken into multiple pieces.
Long Bone Fractures: Particularly in bones like the femur, tibia, or humerus where a curved plate can provide better alignment and stability.
Malunions and Nonunions: Corrective surgeries for fractures that have healed in improper alignment (malunion) or have not healed at all (nonunion).
Periarticular Fractures:
Fractures near joints that require stable fixation to restore joint function and alignment.
Provides support for fractures involving the distal femur, proximal tibia, and other periarticular regions.
Osteoporotic Fractures:
In patients with low bone density, where the locking mechanism of the plate provides enhanced stability and reduces the risk of implant failure.
Pathologic Fractures:
Fractures occurring in bones weakened by disease, such as tumors or infection, requiring strong and stable fixation.
Reconstruction Procedures:
Osteotomies: Surgical cutting of bone for correction of deformities.
Bone Defect Management: Management of bone defects due to trauma or disease.
Revision Surgeries:
Revisions of failed previous fixations or fractures that have not healed properly with non-locking plates.
Trauma:
High-energy fractures resulting from accidents or sports injuries where stable fixation is essential for proper healing and recovery.
Anatomical Fit: The curved design conforms closely to the natural shape of long bones, reducing the need for contouring during surgery.
Stability: Locking screws provide angular stability, crucial for maintaining alignment and promoting bone healing.
Versatility: Offers various sizes and configurations to accommodate different patient anatomies and fracture patterns.
Reduced Soft Tissue Irritation: Low-profile design minimizes irritation to surrounding soft tissues, enhancing patient comfort and recovery.
Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) Capability: Compatible with MIS techniques, which can reduce surgical trauma and accelerate recovery.
The Curved Reconstruction Locking Compression Plate II is designed to provide robust fixation and support in challenging fracture scenarios, contributing to improved patient outcomes and faster rehabilitation. Always consult with a healthcare professional for specific medical advice tailored to individual conditions.
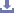
A sacroiliac locking compression plate is a specialized orthopedic implant used for stabilizing fractures, fusions, or injuries involving the sacroiliac joint. It combines compression and locking screw technology to provide stability and promote healing.
Anatomical Fit: Designed to match the contours of the sacroiliac joint anatomy for optimal alignment and stability.
Locking Mechanism: Utilizes locking screws that engage with the plate, providing angular stability and minimizing the risk of screw loosening.
Compression Slots/Holes: Includes slots or holes to allow for compression at the fracture or fusion site, aiding in bone healing.
Biocompatible Material: Typically made from materials like titanium alloy or stainless steel, ensuring compatibility with the human body.
Low-profile Design: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Sacroiliac locking compression plates are used for:
Fracture Fixation: Stabilizing fractures of the sacrum or ilium involving the sacroiliac joint.
Joint Fusion: Facilitating fusion of the sacroiliac joint, typically in cases of sacroiliac joint dysfunction or instability.
The locking mechanism involves screws that engage with threaded holes in the plate, creating a fixed-angle construct. This enhances stability compared to traditional non-locking plates, which rely on friction between the plate and bone.
Enhanced Stability: Provides stable fixation, crucial for fractures or injuries affecting the sacroiliac joint.
Biomechanical Support: Restores biomechanical alignment of the joint, aiding in functional recovery and joint fusion.
Reduced Complications: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and promotes faster healing due to its low-profile design.
Customization: Offers options in size and configuration to meet individual patient needs and surgical requirements.
Yes, some designs of sacroiliac locking compression plates are compatible with minimally invasive surgical techniques, which can reduce soft tissue disruption and improve recovery times.
The duration of implantation depends on various factors, including the patient's healing progress and the specific condition being treated. In some cases, the plates may remain in place permanently if they do not cause discomfort or complications.
Patients can expect a period of recovery and rehabilitation to regain strength and mobility. The plate is designed to support the bone during healing and is typically well-tolerated by the body.
Consult with an orthopedic surgeon who can evaluate your specific condition, imaging studies, and medical history to determine the most appropriate treatment and implant options.
These FAQs provide a general overview of sacroiliac locking compression plates. For specific medical advice and detailed information, always consult with a healthcare professional or orthopedic surgeon.
| Code | Holes | ||||
| 70746-006 | 6 | ||||
Anatomical Design:
Shape and Contour: Designed to fit the anatomy of the sacroiliac joint, ensuring proper alignment and stability.
Material:
Biocompatible: Typically made from materials like titanium alloy or stainless steel, ensuring compatibility with the human body.
Compression Mechanism:
Compression Slots/Holes: Includes slots or holes to allow for compression at the fracture site, aiding in bone healing and stability.
Locking Mechanism:
Locking Screws: Utilizes locking screws that engage with the plate, providing angular stability and reducing the risk of screw loosening.
Plate Thickness and Profile:
Low-profile Design: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Versatility:
Various Sizes: Available in different sizes to accommodate varying patient anatomies and fracture types.
Multiple Holes: Provides flexibility in screw placement to adapt to different fracture patterns and surgical techniques.
Surgical Technique:
Placement: Requires precise surgical placement to ensure proper alignment and effective compression of the joint.
Clinical Application:
Fracture Fixation: Used primarily for stabilizing fractures of the sacrum or ilium involving the sacroiliac joint.
Joint Fusion: Can also be used in procedures aimed at achieving fusion of the sacroiliac joint.
Postoperative Considerations:
Recovery: Patients may undergo physical therapy to regain strength and mobility after surgery.
Long-term Use: In some cases, the plate may remain in place permanently if it does not cause discomfort or complications.
Stability: Provides stable fixation, crucial for fractures or injuries affecting the sacroiliac joint.
Biomechanical Support: Restores biomechanical alignment of the joint, aiding in functional recovery.
Reduced Complications: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and promotes faster healing due to its low-profile design.
Customization: Offers options in size and configuration to meet individual patient needs and surgical requirements.
Always consult with a healthcare professional or orthopedic surgeon for specific medical advice and treatment options related to sacroiliac fractures or injuries.
Complex Fractures:
Comminuted Fractures: Fractures where the bone is broken into multiple pieces.
Long Bone Fractures: Particularly in bones like the femur, tibia, or humerus where a curved plate can provide better alignment and stability.
Malunions and Nonunions: Corrective surgeries for fractures that have healed in improper alignment (malunion) or have not healed at all (nonunion).
Periarticular Fractures:
Fractures near joints that require stable fixation to restore joint function and alignment.
Provides support for fractures involving the distal femur, proximal tibia, and other periarticular regions.
Osteoporotic Fractures:
In patients with low bone density, where the locking mechanism of the plate provides enhanced stability and reduces the risk of implant failure.
Pathologic Fractures:
Fractures occurring in bones weakened by disease, such as tumors or infection, requiring strong and stable fixation.
Reconstruction Procedures:
Osteotomies: Surgical cutting of bone for correction of deformities.
Bone Defect Management: Management of bone defects due to trauma or disease.
Revision Surgeries:
Revisions of failed previous fixations or fractures that have not healed properly with non-locking plates.
Trauma:
High-energy fractures resulting from accidents or sports injuries where stable fixation is essential for proper healing and recovery.
Anatomical Fit: The curved design conforms closely to the natural shape of long bones, reducing the need for contouring during surgery.
Stability: Locking screws provide angular stability, crucial for maintaining alignment and promoting bone healing.
Versatility: Offers various sizes and configurations to accommodate different patient anatomies and fracture patterns.
Reduced Soft Tissue Irritation: Low-profile design minimizes irritation to surrounding soft tissues, enhancing patient comfort and recovery.
Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) Capability: Compatible with MIS techniques, which can reduce surgical trauma and accelerate recovery.
The Curved Reconstruction Locking Compression Plate II is designed to provide robust fixation and support in challenging fracture scenarios, contributing to improved patient outcomes and faster rehabilitation. Always consult with a healthcare professional for specific medical advice tailored to individual conditions.
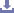
A sacroiliac locking compression plate is a specialized orthopedic implant used for stabilizing fractures, fusions, or injuries involving the sacroiliac joint. It combines compression and locking screw technology to provide stability and promote healing.
Anatomical Fit: Designed to match the contours of the sacroiliac joint anatomy for optimal alignment and stability.
Locking Mechanism: Utilizes locking screws that engage with the plate, providing angular stability and minimizing the risk of screw loosening.
Compression Slots/Holes: Includes slots or holes to allow for compression at the fracture or fusion site, aiding in bone healing.
Biocompatible Material: Typically made from materials like titanium alloy or stainless steel, ensuring compatibility with the human body.
Low-profile Design: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Sacroiliac locking compression plates are used for:
Fracture Fixation: Stabilizing fractures of the sacrum or ilium involving the sacroiliac joint.
Joint Fusion: Facilitating fusion of the sacroiliac joint, typically in cases of sacroiliac joint dysfunction or instability.
The locking mechanism involves screws that engage with threaded holes in the plate, creating a fixed-angle construct. This enhances stability compared to traditional non-locking plates, which rely on friction between the plate and bone.
Enhanced Stability: Provides stable fixation, crucial for fractures or injuries affecting the sacroiliac joint.
Biomechanical Support: Restores biomechanical alignment of the joint, aiding in functional recovery and joint fusion.
Reduced Complications: Minimizes soft tissue irritation and promotes faster healing due to its low-profile design.
Customization: Offers options in size and configuration to meet individual patient needs and surgical requirements.
Yes, some designs of sacroiliac locking compression plates are compatible with minimally invasive surgical techniques, which can reduce soft tissue disruption and improve recovery times.
The duration of implantation depends on various factors, including the patient's healing progress and the specific condition being treated. In some cases, the plates may remain in place permanently if they do not cause discomfort or complications.
Patients can expect a period of recovery and rehabilitation to regain strength and mobility. The plate is designed to support the bone during healing and is typically well-tolerated by the body.
Consult with an orthopedic surgeon who can evaluate your specific condition, imaging studies, and medical history to determine the most appropriate treatment and implant options.
These FAQs provide a general overview of sacroiliac locking compression plates. For specific medical advice and detailed information, always consult with a healthcare professional or orthopedic surgeon.
